If you are struggling to understand the has_many through in rails, I am confident that these three sections will help you have a clear idea on why we use and when to use this helper.
-
Understanding the fundamentals of the many to many relationship in the relational database management system(RDMB) specially the join table.
-
We’ll Create an example where we’ll add basic functionalities(Create/Delete) without using the has_many through.
-
Then add the helper and refactor the code.
Understanding the many to many relationship
Let’s take an Ecommerce business as an example where we have products and orders.
A user can place an order with many products, and a product can be in many orders, so it’s a many to many relationship between the order and the product.
Now let’s represent this relationship.
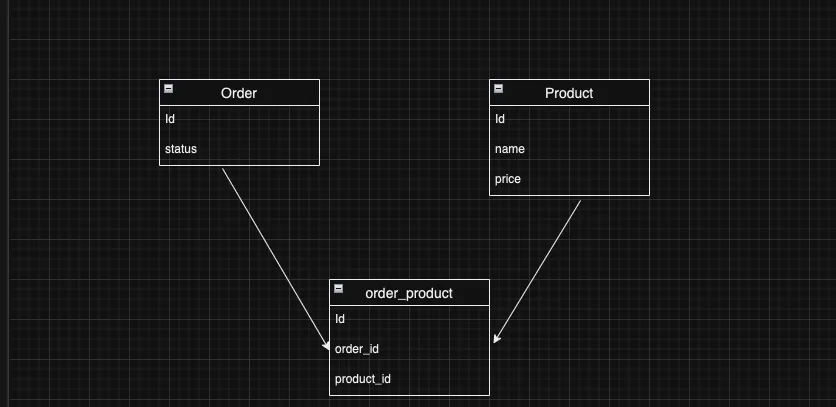
In the RDBM the only way to represent this is by creating a new table(Joining table or Join table), this table will have two columns the order_id and the product_id. Let’s name this table order_product (It’s a convention to name the table by combining the two other table names).
To visualize how this relationship works, let’s make a small example. A customer created an order with 4 products, order_id is 3 and products_ids are (1 | 2 | 3 |4).
In our order_product table we will insert 4 rows with order_id of 4 and with the relevant product_id.

Now when we’ll query the order products, we have to filter the products based on the order_id = 3.
To learn more about the many to many relationship, I encourage you to read this article. https://dzone.com/articles/how-to-handle-a-many-to-many-relationship-in-datab
Now let’s Code it.
Create a Rails project with the models and associations
In this section, we’ll create a rails project and generate three models order, product, and the join table order_product.
First, go and create a new rails project, when the project is created let’s generate the models.
First, go and create a new rails project, when the project is created let’s generate the models.
rails generate model order status:string user:references
rails generate model product name:string price:decimal
rails generate model order_product order:references product:references
Finally, run rails db:migrate to create our tables in the DB.
Remember that the main association is between products and orders by using the join table order_product, so the orders and products will have many order_product, but the order_product model will belong to both orders and products. Let’s add it!
class Order < ApplicationRecord
has_many :order_product
end
class Product < ApplicationRecord
has_many :order_product
end
class OrderProduct < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :order
belongs_to :product
end
Now let’s Jump into the command line and start adding functionalities. Open the console rails console and first let’s generate some data
50.times do
Product.create(name: “product_name”, price: 10)
end
10.times do
order = orders.create()
5.times do
OrderProduct.create(order_id: order.id, product_id: Product.find(rand(1...50).id))
end
end
This will generate 50 products and 10 orders each order with 5 products.
Adding basic functionalities without has_many through
The functionalities that we’ll add are
- Query all the products in an order
- Adding a product to an order
Query all the products from the order
first, let’s get the order id we want to query the products from
order_id = Order.first.id
Then we will query the data from the OrderProduct by passing the order_id and mapping through the data to return just the product.
OrderProduct.where(order_id: order_id).map {|item| item.product }
Adding a product to an order
order_id = Order.first.id
product_id = Product.find(20)
OrderProduct.create(order_id: order_id, product_id: product_id)
Whenever we want to query or insert a product we need to use the OrderProduct model and pass the required parameters, when using the has_many through method we won’t need to use it anymore and the code will be much simpler and cleaner.
Using the has_many through
Let’s add the method to model/order.rb
class Order < ApplicationRecord
has_many :order_product
has_many :products, through: :order_product
end
Let’s jump to the rails console again(refresh the rails console using reload! command.)
Query all the products from the order
Order.first.products
Adding a product to an order
Order.first.products << Product.find(22)
Sweet, no more interacting with the join model.
Conclusion
The rails documentation is the best place to learn, but sometimes to understand the use of a certain method you must create an example with and without the method this way you will have a deep knowledge than just reading about it.
Thanks for reading !!